How to Upgrade to a Premium Account in Minecraft 2021
How to have a Premium Account in Minecraft If you’re an avid Minecraft player, you may be wondering how to upgrade to a premium account in 2021. …
Read Article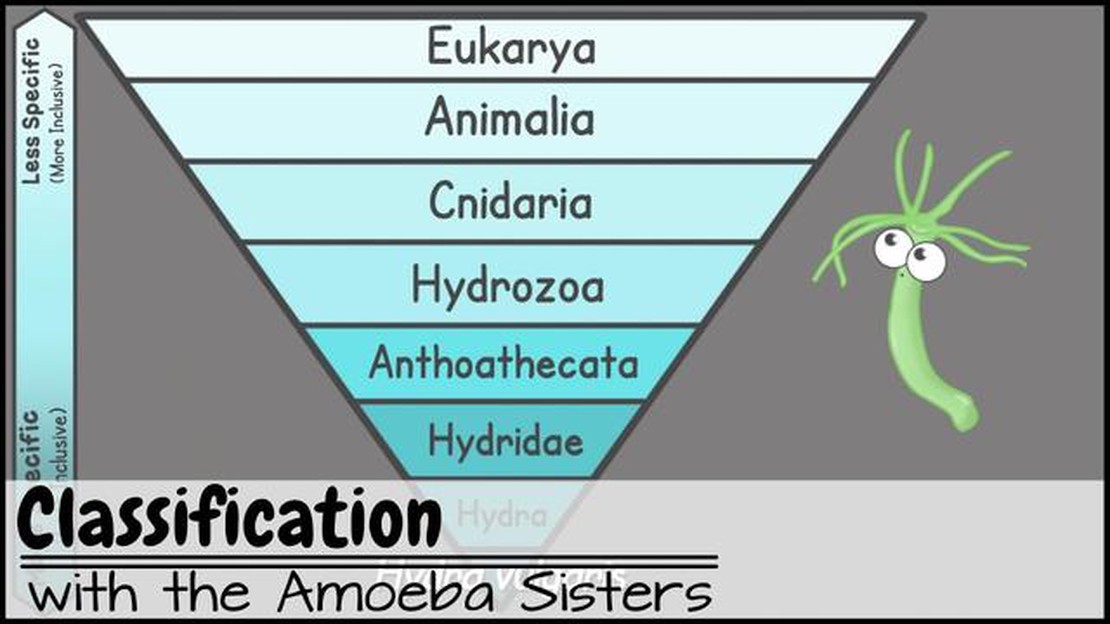
Taxonomy is a scientific discipline that plays a fundamental role in our understanding of the relationships among organisms on Earth. By categorizing and classifying organisms based on their shared characteristics, taxonomy allows us to organize and make sense of the immense diversity of life on our planet. It provides a framework for studying the evolutionary history and genetic relationships among different species, helping scientists unravel the mysteries of life’s interconnectedness.
At its core, taxonomy is about discovering and documenting the unique and shared traits among organisms. Taxonomists strive to classify organisms into groups known as taxa, which range from broad categories like kingdoms to more specific classifications like species. By studying and comparing these traits, taxonomists can determine the evolutionary relationships between species and trace their ancestry back to a common ancestor.
One of the key benefits of taxonomy is its ability to provide a systematic way of naming and organizing species. Through the use of binomial nomenclature, each species is given a unique, two-part Latin name that reflects its genus and species. This standardized naming system allows scientists from different countries and fields to communicate unambiguously about specific organisms. It also enables researchers to easily search and reference information about a particular species, aiding in the sharing of knowledge and collaborative efforts in scientific research.
Taxonomy is the science of classifying and categorizing organisms based on their characteristics and evolutionary relationships. It provides a systematic way to understand the diversity, relationships, and evolutionary history of all living organisms on Earth, from microscopic bacteria to complex plants and animals.
Taxonomy helps us organize and name organisms in a way that reflects their evolutionary relatedness. By studying the similarities and differences between organisms, taxonomists can group them into categories and assign them scientific names. This classification system allows scientists to communicate and share information about organisms more efficiently.
One of the main goals of taxonomy is to develop a hierarchical system of classification, known as a taxonomy. This system organizes organisms into different levels, or taxa, based on their shared characteristics. The highest level of classification is the domain, followed by kingdom, phylum, class, order, family, genus, and species. Each taxonomic level represents a different degree of relatedness between organisms.
Taxonomy also helps us understand the evolutionary relationships between organisms. By studying the similarities and differences in their physical characteristics, genetic makeup, and behavior, taxonomists can infer how different species are related to each other and how they have evolved over time. This information is crucial for understanding the history of life on Earth and how different organisms have adapted to their environments.
Furthermore, taxonomy plays a crucial role in conservation biology and biodiversity studies. By identifying and cataloging different species, taxonomists can determine which ones are endangered or at risk of extinction. This information is essential for developing conservation strategies and protecting the Earth’s biodiversity.
In conclusion, taxonomy is essential for understanding the relationships among organisms on Earth. It provides a framework for organizing and naming organisms based on their characteristics and evolutionary history. By studying taxonomy, scientists can gain valuable insights into the diversity, evolution, and conservation of life on our planet.
Taxonomy is a scientific discipline that categorizes and classifies organisms based on their shared characteristics and evolutionary relationships. It is crucial in understanding the relationships among organisms on Earth, as it provides a systematic way to organize and study biodiversity.
Organization and Classification: Taxonomy allows scientists to organize and classify organisms into hierarchical categories, ranging from broad kingdoms to specific species. This classification system helps to categorize and group organisms based on their shared characteristics, making it easier to study and compare different species.
Identifying New Species: Taxonomy plays a crucial role in discovering and identifying new species. By analyzing an organism’s characteristics and comparing it to known species, taxonomists can determine whether it is a new species or a variation of an existing one. This information is essential for documenting and conserving biodiversity.
Understanding Evolutionary Relationships: Taxonomy helps in understanding the evolutionary relationships among organisms. By comparing the similarities and differences in their characteristics, scientists can infer the evolutionary history and determine how different species are related to each other. This knowledge provides insights into the common ancestry and evolutionary processes that have shaped the diversity of life on Earth.
Conservation and Management: Taxonomy is essential for conservation and management efforts. By identifying and categorizing species, scientists can assess their conservation status and prioritize conservation actions. Taxonomy also helps in understanding the ecological roles of different organisms and their interactions within ecosystems, which is crucial for effective ecosystem management.
Communication and Collaboration: Taxonomy provides a standardized language for communication among scientists. By using the same classification system, scientists from different disciplines and regions can easily share and compare their research findings. This collaboration is essential in advancing our understanding of the relationships among organisms on Earth.
Read Also: Ultimate Guide: How To Play Chang'e Mobile Legends 2022 - Tips & Strategies
Economic and Medical Importance: Taxonomy has significant economic and medical implications. By identifying and classifying organisms, scientists can identify potential sources of food, medicine, and other valuable resources. Additionally, taxonomy helps in the identification of harmful organisms, such as pathogens and invasive species, facilitating the development of strategies for their control and prevention.
In conclusion, taxonomy is crucial in understanding the relationships among organisms on Earth. It helps in organizing, identifying, and classifying organisms, providing insights into their evolutionary relationships and facilitating conservation efforts. Without taxonomy, our understanding of the diversity and interconnectedness of life on Earth would be limited.
Taxonomy plays a crucial role in understanding the relationships among organisms on Earth. It involves the classification and organization of living organisms based on their characteristics and evolutionary relationships. Through taxonomy, scientists can identify and categorize organisms, allowing for a better understanding of their similarities and differences.
Classification:
Classification is the process of grouping organisms into categories based on their shared characteristics. Taxonomists use a hierarchical system of classification that starts with larger, more general groups and narrows down to smaller, more specific groups. This system is known as the taxonomic hierarchy and includes seven categories:
Organization:
Read Also: AI Image Generator Creates the Terrifying 'First Cryptid of the Latent Space'
Taxonomy provides a systematic way to organize the diversity of life on Earth. By grouping organisms into categories, scientists can easily compare and contrast different species and study their evolutionary relationships. The hierarchical nature of taxonomy allows for the organization of large amounts of data, making it easier to understand and communicate information about organisms.
Evolutionary Relationships:
Taxonomy helps scientists understand the evolutionary relationships among organisms. By examining similarities and differences in their characteristics, taxonomists can determine how different species are related and how they have evolved over time. This information is crucial for studying biodiversity, understanding the history of life on Earth, and predicting the impact of environmental changes.
Taxonomic Tools:
Various tools and techniques are used in taxonomy to classify and organize living organisms. These include morphological analysis (study of physical characteristics), molecular biology (study of genetic material), and cladistics (analysis of shared characteristics). Advances in technology, such as DNA sequencing, have greatly improved the accuracy and efficiency of taxonomic classification.
In conclusion, taxonomy plays a vital role in understanding the relationships among organisms on Earth. Through classification and organization, scientists can study the similarities and differences among species, explore their evolutionary relationships, and gain insights into the diversity of life on our planet.
Taxonomy, the science of classifying and categorizing organisms, is an essential tool in biology and has numerous applications that extend beyond the field. By organizing and naming species, taxonomy helps in understanding relationships among organisms on Earth and enables various practical uses:
In conclusion, taxonomy has diverse applications in biology and beyond. From species identification to biodiversity conservation and medicine to agriculture, taxonomy provides the foundation for understanding and managing the complex relationships among organisms on Earth.
Taxonomy is the science of classifying and categorizing organisms based on their characteristics and evolutionary relationships. It is important in understanding relationships among organisms because it allows scientists to identify and group organisms based on shared traits, helping them to study and understand the diversity and evolutionary history of life on Earth.
Taxonomy helps in identifying new species by providing a framework for classifying and categorizing organisms. New species can be identified by comparing their characteristics to known taxa and determining if they fit into an existing classification or if they represent a new species. By using taxonomy, scientists can assign a unique name and classification to newly discovered organisms.
The different levels of classification in taxonomy are domain, kingdom, phylum, class, order, family, genus, and species. These levels represent a hierarchical system, with each level encompassing a group of organisms that share certain characteristics. The species level is the most specific, representing a group of organisms that can interbreed and produce fertile offspring.
Taxonomy helps in understanding evolutionary relationships among organisms by grouping organisms based on their shared characteristics and evolutionary history. By studying the similarities and differences between different taxa, scientists can infer the evolutionary relationships among organisms and construct phylogenetic trees, which depict the evolutionary history and relatedness of different species.
Taxonomists face several challenges in classifying and categorizing organisms. One challenge is the existence of cryptic species, which are morphologically similar but genetically distinct. Taxonomists also encounter difficulties in classifying organisms with complex life cycles or those that exhibit variation in their characteristics. Additionally, there is a lack of funding and resources for taxonomic research, making it challenging to comprehensively study and classify all organisms on Earth.
The field of taxonomy has evolved over time, particularly with the advancement of molecular techniques and DNA sequencing. These techniques have allowed taxonomists to study the genetic makeup of organisms and use molecular data to infer evolutionary relationships and classify organisms. Additionally, technology has enabled the creation of digital databases and online resources that facilitate the sharing and accessibility of taxonomic information.
How to have a Premium Account in Minecraft If you’re an avid Minecraft player, you may be wondering how to upgrade to a premium account in 2021. …
Read ArticleWhen Is Roblox Coming To Ps4? Roblox, a popular online gaming platform, has gained immense popularity on various platforms such as PC, mobile devices, …
Read ArticleCult of the Lamb review Indie game enthusiasts have been eagerly awaiting the release of Cult of the Lamb, the upcoming game developed by Massive …
Read ArticleWhat To Do With Turnips In Animal Crossing? Turnips are a valuable resource in the hit video game Animal Crossing. These vegetable-based items can be …
Read ArticleShould I use a TV as a computer monitor? With the rise of smart TVs and high-resolution displays, many people are wondering if they should use a TV as …
Read ArticleHere’s how to bring Space Cadet 3D Pinball back to Windows Remember the classic game Space Cadet 3D Pinball? For many of us, it was a childhood …
Read Article