Learn the Top Hacks to Master Roblox | Easy and Effective Methods
How To Hack Roblox? Are you tired of getting stuck in Roblox and not being able to advance to the next level? Don’t worry, we’ve got you covered! With …
Read Article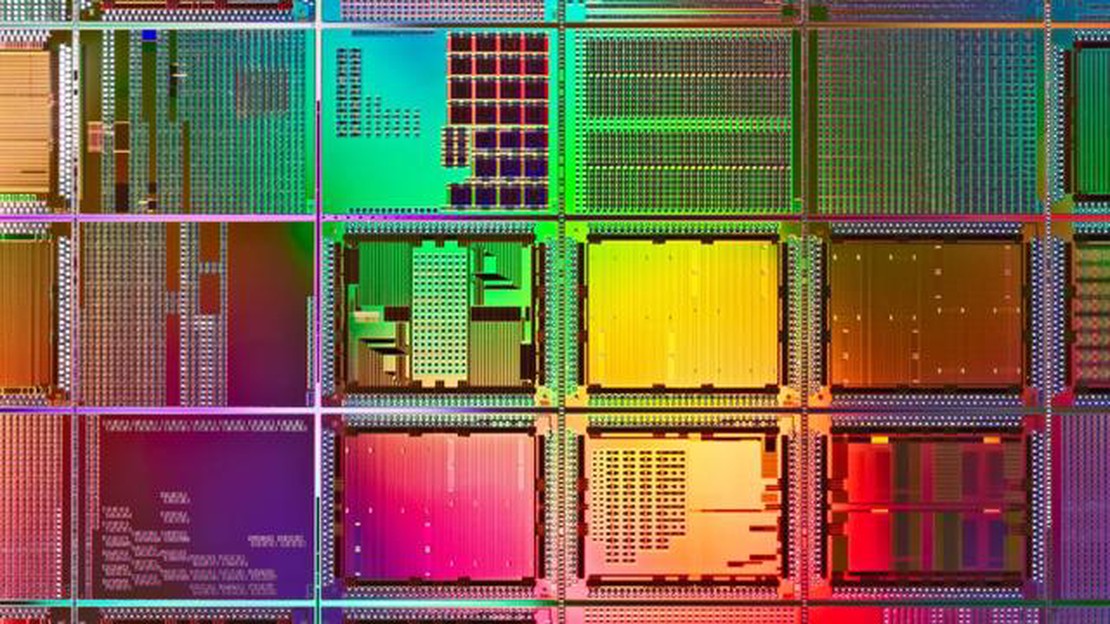
Intel, the leading manufacturer of computer chips, has recently announced its ambitious plan to include one trillion transistors on their chips by the year 2030. This groundbreaking development is set to revolutionize the field of microelectronics and pave the way for even more powerful and efficient computers.
The transistor, a fundamental component of modern electronics, is responsible for controlling the flow of electrical current in integrated circuits. The more transistors a chip has, the more data it can process and the faster it can perform calculations. Currently, Intel’s most advanced chips contain billions of transistors, but the company aims to increase this number a thousandfold in just a decade.
This achievement will be made possible by advances in nanotechnology, a field that focuses on manipulating matter at the atomic and molecular scale. Intel plans to use new materials and innovative manufacturing techniques to create transistors that are even smaller and more efficient than those currently in use. These advancements will not only increase the number of transistors on each chip, but also improve their performance and energy efficiency.
Intel’s prediction of one trillion transistors on chips by 2030 reflects the company’s commitment to pushing the boundaries of technology. By continually innovating and striving for greater processing power, Intel aims to meet the growing demand for faster and more powerful computers in an increasingly digital world.
Intel, one of the leading semiconductor companies in the world, has made an astounding prediction for the future of computer chips. According to their projection, by the year 2030, chips will be capable of accommodating an incredible one trillion transistors. This ambitious advancement in technology has the potential to revolutionize the computing industry and enable a wide range of new applications.
Transistors are the fundamental building blocks of modern electronic devices. They act as switches that control the flow of electrical current within a chip, enabling the processing and storage of information. Over the years, the number of transistors that can be packed onto a single chip has been steadily increasing, following a trend known as Moore’s Law.
Moore’s Law, named after Intel co-founder Gordon Moore, states that the number of transistors on a chip doubles approximately every two years. This rapid pace of progress has been a driving force behind the exponential growth in computing power and the shrinking size of electronic devices. However, as transistors approach their physical limitations, maintaining this trend has become increasingly challenging.
Intel’s prediction of one trillion transistors on chips by 2030 represents a significant milestone in pushing the limits of Moore’s Law. Achieving this feat would require overcoming several technological hurdles, including developing new materials and manufacturing techniques. Intel and other chip manufacturers are actively researching and investing in breakthroughs that can make this vision a reality.
With the tremendous increase in transistor density, future chips could offer unprecedented computational capabilities. This could lead to advancements in artificial intelligence, data processing, and energy efficiency, among other areas. Additionally, the proliferation of Internet of Things (IoT) devices could benefit from the ability to pack more functionality into smaller and more power-efficient chips.
However, the realization of one trillion transistors on chips is not without its challenges. Increasing transistor density can result in higher power consumption and heat generation, requiring innovative cooling solutions. Moreover, the cost and complexity of designing and manufacturing such chips may pose significant barriers.
In conclusion, Intel’s projection of one trillion transistors on chips by 2030 represents an ambitious goal that could reshape the future of computing. While there are obstacles to overcome, the potential benefits in terms of enhanced computing power and new applications are vast. As technology continues to evolve, the semiconductor industry will be at the forefront of innovation, driving progress in various fields.
Intel, one of the world’s leading semiconductor manufacturers, has recently announced its ambitious goal to reach one trillion transistors on chips by the year 2030. This milestone is expected to revolutionize the field of chip technology and open up new possibilities for the world of computing.
For decades, Intel has been at the forefront of chip technology, constantly pushing the boundaries of what is possible. The number of transistors on a chip has been a key metric in measuring the progress of chip technology, and Intel’s announcement marks a significant leap forward.
Transistors are tiny electronic devices that act as switches, allowing the flow of electrical current or blocking it. They are the building blocks of modern electronic devices, enabling the processing and storage of data. The more transistors that can be packed onto a chip, the more powerful and efficient the chip becomes.
Intel’s planned achievement of one trillion transistors on chips by 2030 represents a ten-fold increase compared to the current technology. This ambitious goal will require major advancements in manufacturing processes and materials science.
Read Also: Discover the Exciting Activities in Animal Crossing at Night
By packing more transistors onto a single chip, Intel aims to improve performance, increase energy efficiency, and enable new capabilities in areas such as artificial intelligence, machine learning, and high-performance computing. The ability to process and analyze massive amounts of data in real-time has the potential to transform various industries and drive innovation.
Intel’s announcement reflects the continuous innovation and dedication to advancements in chip technology. As the demand for computing power continues to grow, Intel’s goal to achieve one trillion transistors on chips by 2030 will be a significant milestone that propels the industry forward and shapes the future of technology.
Read Also: Lollipop Chainsaw Remake Set to Launch in 2022
As technology continues to advance at a rapid pace, the future of computing hardware looks promising. With Intel predicting one trillion transistors on chips by 2030, we can expect significant improvements in performance and capabilities.
Transistors are the building blocks of modern computer chips, and the ability to fit one trillion transistors onto a single chip is a remarkable achievement. This increase in transistor count will enable faster processing speeds, higher memory capacities, and more efficient power consumption.
One of the key benefits of this advancement is the development of more powerful artificial intelligence (AI) systems. With an abundance of transistors, AI algorithms can be run more efficiently and effectively. This will lead to improved machine learning capabilities and enhanced decision-making processes.
Additionally, the increase in transistor count will allow for the development of more complex and sophisticated applications. Virtual reality (VR), augmented reality (AR), and mixed reality (MR) technologies will be able to deliver more immersive and realistic experiences. We can expect to see advancements in gaming, training simulations, and medical imaging.
Furthermore, the future of computing hardware will also bring about advancements in data storage. With one trillion transistors, we can expect larger and faster storage devices. This will benefit data-intensive industries such as cloud computing, big data analytics, and video streaming services.
However, with these advancements comes the challenge of heat dissipation. As the number of transistors increases, so does the amount of heat generated. Designing efficient cooling systems will be crucial to ensure the longevity and performance of these future hardware technologies.
In conclusion, the future of computing hardware is set to be exciting and transformative. With the prediction of one trillion transistors on chips by 2030, we can expect faster processing speeds, higher memory capacities, and more powerful AI systems. This will pave the way for advancements in virtual reality, data storage, and other industries that rely on computational power. It is an exciting time to be a part of the ever-evolving world of technology.
Intel predicts that there will be one trillion transistors on chips by 2030.
Intel is making this prediction based on the continuous advancement and development of semiconductor technology and their ability to scale chip manufacturing processes.
Having one trillion transistors on chips would allow for more powerful and efficient processing capabilities, enabling advancements in artificial intelligence, data analysis, and other computationally intensive tasks.
Chips with one trillion transistors would have significantly higher processing power and efficiency compared to current chips, which typically contain tens of billions of transistors.
Achieving one trillion transistors on chips could pose challenges in terms of manufacturing capabilities, thermal management, power consumption, and overall chip design complexity.
While it is difficult to predict the exact timeline, it is possible that chips with one trillion transistors will be available to the general public by 2030, especially in areas such as high-performance computing and data centers.
How To Hack Roblox? Are you tired of getting stuck in Roblox and not being able to advance to the next level? Don’t worry, we’ve got you covered! With …
Read ArticleElden Ring: Where to find the Seppuku Ash of War Are you ready to explore the vast and treacherous world of Elden Ring? Prepare yourself for an …
Read ArticleThe Cycle: Frontier map: What you need to know to survive The Cycle: Frontier is an online multiplayer game set in a distant future where players …
Read ArticleThe best pixel art tools for making your own game Pixel art has become increasingly popular in the world of gaming. It offers a nostalgic and unique …
Read ArticleWhere to find spells in Elden Ring As you traverse the vast and dangerous world of Elden Ring, you will come across various challenges that require …
Read ArticleHow To Use Baby Dragon In Clash Of Clans? Are you struggling to maximize the potential of the Baby Dragon in Clash of Clans? This versatile and …
Read Article